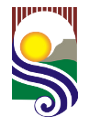
White Top
Quick Facts…
- is a deep-rooted perennial that reproduces by seed and root.
- flowers from May through June and begins producing seeds by July. A single plant can produce between 1,200 to 4,800 seeds that can remain viable in the soil for up to three years.
- will be consumed by sheep when the plant is young. Cattle that are exposed to this weed (alfalfa) will produce tainted milk. Most livestock tend to avoid this weed while grazing.
- infestations occur, 90 percent of the time, in disturbed areas. Roadside grading can spread the plant one mile in a single year.
Control
- Digging can provide control of small infestations if the entire root is removed. This should occur within 10 days of emergence throughout the growing season.
- Hand pulling, in general, is not effective because the root system may not be entirely removed.
- Cultivation is the major factor for the spread of the plant because root fragments will be left behind, producing new plants. The only way cultivation can be effective is if it’s repeated frequently throughout the growing season for several years.
- Frequent mowing can remove biomass, seed production, and shoots produced. Plants that were mowed during flowering produced fewer viable seeds than plants that were mowed during bolting.
- Herbicides can be used to control this weed, but success can be difficult. Non-crop products like Escort and Telar have proven to be the most effective. Other products such as those containing 2,4-D or Dicamba have also been used. Applications made when the weed is at the bud through flower stage will translocate better to the roots and rhizomes, however, annual treatments may be necessary. Always read and follow the label when using any herbicide.